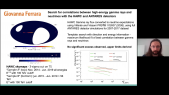
Detection of emission from Cygnus Cocoon above 100TeV with LHAASO
-
299 views
-
4 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 7, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 15. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/98542982538
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 98542982538
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/44-The-Origins-of-Galactic-Cosmic-Rays-GAD-GAI-CRD/125
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-04/5
Abstract:
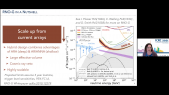
'The energy spectrum of cosmic rays implies that our Galaxy contains PeV proton accelerators (PeVatrons). However, the origin of PeV cosmic rays is still an open question. Star forming regions (SFR) have long been advised as ideal candidates of PeV cosmic ray accelerators. The gamma-ray radiation of Cygnus Cocoon measured by Fermi-LAT may be produced by newly accelerated cosmic rays from Cygnus OB2, which is an example of gamma-ray emission associated with SFR. Benefiting from the best sensitivity above tens of TeV, LHAASO has successfully detected an extended gamma-ray source spatially coincident with Cygnus Cocoon with a significance exceeding 10sigma above 100TeV. The energy spectrum from 10TeV to PeV is studied. Detailed morphological studies can give us a deeper understanding of the acceleration and transport of particles around the OB2 cluster.'
Authors: Li Cong | SongZhan Chen | Sha Wu | Ruoyu Liu | Ruizhi Yang
Collaboration: Lhaaso
Indico-ID: 878
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/843
Li Cong