Development of the Solar Neutron TRACking (SONTRAC) Concept
-
106 views
-
1 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 5, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 16. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://icrc2021.desy.de/pf_access_abstracts
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/Presenter-Forum-1-Evening-All-Categories/48
Abstract:
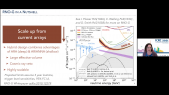
'Fast neutrons ( larger 0.5 MeV) are ubiquitous in nature, originating from nuclear interactions in environments including the solar corona, within planetary atmospheres, and in the lunar regolith. However, measurements of fast neutrons of solar origin are extremely limited due to the challenges imposed by high backgrounds and the relatively short lifetime of free neutrons before they undergo beta decay. Traditional double-scatter neutron spectrometers require an incident neutron to elastically scatter in two widely spaced detectors, allowing the reconstruction of the incident neutron’s energy and direction onto an annulus. While double-scatter spectrometers are well-proven, they suffer from low effective area due to spacecraft size constraints as well as limited resolution due to the possibility of the recoil protons escaping the detector volume. The Solar Neutron TRACking (SONTRAC) concept overcomes these limitations through the use of stacked planes of plastic scintillating fibers arranged in an orthogonal configuration, to measure the ionization tracks of recoil protons. The recoil protons’ energy and direction supplant the need to measure the neutron’s time-of-flight between detectors, thereby dramatically increasing the effective area and detection efficiency. SONTRAC employs modern, miniature silicon photomultipliers (SiPM) to measure the light output from the fibers. SiPMs offer significant advantages over other photodetectors such as photomultiplier tubes due to their compact size and low bias voltages. The SONTRAC concept, combined with recent developments, including the development of a new fiber-bundle without an epoxy binder, testing of new high-performance application-specific-integrated-circuits, and development of new readout and reconstruction techniques are presented.'
Authors: J. Grant Mitchell
Co-Authors: Georgia de Nolfo | Alessandro Bruno | Jeffrey Dumonthier | Iker Liceaga-Indart | Jason Link | Jason Legere | Richard Messner | James Ryan | George Suarez | Teresa Tatoli
Indico-ID: 698
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/1250
J. Grant Mitchell