The Upgrade of Horizon-T Detector
-
51 views
-
0 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 1, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 16. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://icrc2021.desy.de/pf_access_abstracts
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/Presenter-Forum-1-Evening-All-Categories/48
Abstract:
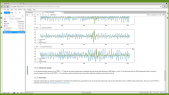
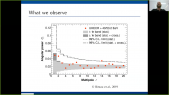
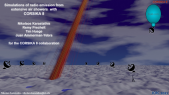
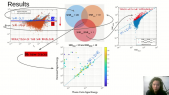
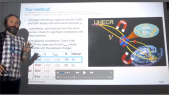
'The Horizon-T experiment is located at the elevation of 3346 m above sea level near the city of Almaty, Republic of Kazakhstan. A thorough comparison of the spatial and temporal characteristics of charged components of Extended Air Showers (EAS) with delayed particles with the simulated EAS using CORSIKA simulation package has been conducted using the selection from the experimental data set of events with two pulses recorded by a detector at ~600 m distance from axis [1]. This comparison has shown that events with delayed particles cannot be described within existing simulation models.rnrnThe significance of these results prompted the upgrade of the Horizon-T experiment. New points have been added at the ~600m to enhance data at that distance. Fast glass-based detectors have been added to the detector center point for accurate measurements of the pulse widths with radiative material layer option. This poster covers these upgrades and the latest data statistics from the new Horizon-T detector from the physics run 2020-2021.rnrn[1] Rashid Beisembaev, et al., 2019. “Extensive Air Showers with Unusual Spatial and Temporal Structure.” In EPJ Web Conf., 208: Pp. 06002.'
Authors: Dmitriy Beznosko
Collaboration: Horizon-T
Indico-ID: 37
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/182
Dmitriy Beznosko