A study on the cosmic ray intensity variation using scintillation counters for air shower observation.
-
131 views
-
3 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 7, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 15. July 2021 - 12:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/22-Atmospheric-effects-of-CR-SH/122
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-07/8
Abstract:
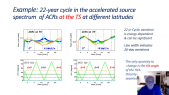
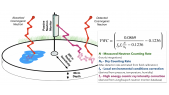
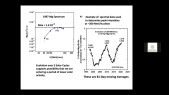
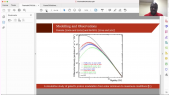
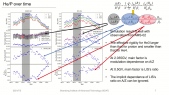
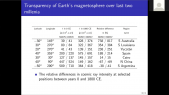
"We report a study on the conversion of a giant cosmic ray observatory for air shower observation to observe cosmic ray intensity variations caused by solar activity, anisotropy associated with interplanetary disturbances, and detection of sudden cosmic ray events on the earth's surface. In this report, we use data from the surface detectors operated by the Telescope Array experiment located at 39^{circ}N, 112^{circ}W (total detector area: 2250 m^{2}). In order to evaluate the cosmic ray intensity variations, we will compare the data with some of the corrections considered and with available world wide database such as Nagoya Muon detector and other observatories that have been in stable operation at different geographic longitudes. Finally, we will report on the intensity variations due to weather and solar activity recorded during the observation period."
Authors: Katsuya Yamazaki | Toshiyuki Nonaka | Akitoshi Oshima
Co-Authors: for the GRAPES-3 collaboration | for the Telescope Array Collaboration
Collaboration: Telescope ArrayGRAPES-3
Indico-ID: 1058
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/1255
Toshiyuki Nonaka