Acceleration of ultra-high energy cosmic rays in the early afterglows of gamma-ray bursts
-
105 views
-
2 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 6, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 20. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/92210078166
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 92210078166
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/11-UHECR-Acceleration-CRI/83
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-03/4
Abstract:
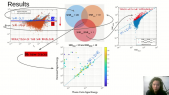
'The origin of ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays (UHECRs) still remains mystery. It has been suggested that UHECRs can be produced by the stochastic acceleration in relativistic jets of gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) at the early afterglow phase. Here, we propose a time-dependent model for proton energization by cascading compressible waves in GRB jets with concurrence of the jet’s dynamics and the mutual interactions between turbulent waves and particles. With the assumption of an initial turbulent injection spectrum W(k) ∝ k^(−3/2) and interstellar medium (ISM) for circumburst environment, our numerical results suggest that protons can be accelerated up to 10^19 eV at the early afterglow. An estimation shows UHE nuclei can easily survive photodisintegration in the external shocks in most cases, thus allowing the acceleration of 10^20 eV cosmic rays in the proposed frame. The spectral slope can be as hard as dN/dE ∝ E^0, which is consistent with the requirement for the interpretation of intermediate-mass composition of UHECR as measured by the Pierre Auger Observatory.'
Authors: Zhang Ze-Lin | Liu Ruo-Yu | Wang Xiang-Yu
Collaboration: Nanjing University
Indico-ID: 29
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/423
Zhang Ze-Lin