Estimation of the exposure of the TUS space based cosmic ray observatory
-
59 views
-
1 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 6, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 16. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://icrc2021.desy.de/pf_access_abstracts
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/Presenter-Forum-1-Evening-All-Categories/48
Abstract:
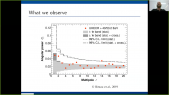
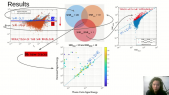
'The TUS observatory, as a part of the JEM-EUSO program, aimed at the detection of Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays (UHECR). TUS was the first UHECR detector to operate in space and was launched on April 28th 2016 from the Vostochny cosmodrome in Russia. It operated until December 2017 and collected ~80000 events with a time resolution of 0.8 μs. A fundamental parameter to be determined for the measurement of cosmic rays properties is the exposure. Such a parameter is important to estimate the average expected event rate as a function of energy and to calculate the absolute flux in case of event detection. We present here a study for the determination of the exposure that TUS accumulated during its flight. The role of clouds, detector dead time, man made sources, storms, lightning discharges, airglow and moon phases is studied in detail. An exposure estimate with its dependence on the energy and with its geographical distribution is presented. We report on the applied technique and on the perspectives of this study in view of future missions of the JEM-EUSO program.'
Authors: Francesco Fenu
Co-Authors: Mikhail Zotov | Kenji Shinozaki | Mario Bertaina | Pavel Klimov | for the JEM-EUSO collaboration
Collaboration: JEM-EUSO
Indico-ID: 752
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/333
Francesco Fenu