Modeling intrinsic time-lags in flaring blazars in the context of Lorentz Invariance Violation searches
-
109 views
-
1 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 5, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 20. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/57-New-Physics-CRD-CRI-DM-GAD-GAI-NU-MM-SH/90
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-07/8
Abstract:
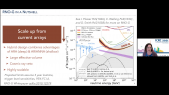
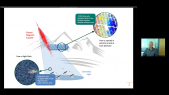
"Some Quantum Gravity (QG) theories, aiming at unifying general relativity and quantum mechanics, predict an energy-dependent modified dispersion relation for photons in vacuum leading to a Violation of Lorentz Invariance (LIV). One way to test these theories is to monitor TeV photons time-of-flight emitted by distant, highly energetic and highly variable astrophysical sources such as flaring active galactic nuclei. Only one time-lag detection was reported so far. We have recently shown however that significant intrinsic time-lags should arise from *in situ* blazar emission processes at TeV energies and should consequently interfere with LIV searches.rnIn this contribution we will review how intrinsic time delays and LIV-induced propagation effects simultaneously contribute to modify blazars' observed spectral energy distributions and lightcurves. Using a time-dependent model, we provide predictions on both contributions for different emission scenarii. We will also introduce hints and methods on how to disentangle intrinsic time delays from extrinsic ones in order to highlight LIV effects."
Authors: Christelle Levy
Co-Authors: Julien Bolmont | Hélène Sol
Collaboration: H.E.S.S.CTA
Indico-ID: 162
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/907
Christelle Levy