The azimuthal distribution of thunderstorm events recorded by the GRAPES-3 experiment
-
103 views
-
5 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 3, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 19. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/92210078166
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 92210078166
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/09-Atmospheric-and-geophysical-phenomena-CRI/68
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-03/4
Abstract:
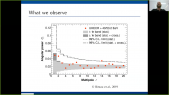
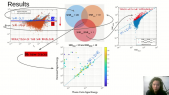
'The GRAPES-3 experiment reported the measurement of 1.3 GV potential across one of the massive thunderclouds recorded on 1 December 2014 by making use of the muon imaging technique. This measurement is ten times larger than the maximum potential reported previously by balloon and rocket sounding measurements, verifying the almost a century old prediction by C.T.R. Wilson. These measurements rely on the precise estimate of the change in the angular muon flux caused by the acceleration of muons during their passage through the charged layers of thunderstorms. The electric potential is estimated with the help of Monte Carlo simulations by using CORSIKA and other in-house tools. A study of the thunderstorms events recorded since April 2011 displays an asymmetry in their azimuthal distribution which can be understood to be caused by the ratio of $mu^+$/$mu^-$.'
Authors: Balakrishnan Hariharan
Collaboration: GRAPES-3
Indico-ID: 1102
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/378
Balakrishnan Hariharan