Study of the solar modulation for the cosmic ray isotopes with the PAMELA experiment
-
79 views
-
0 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 5, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 16. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://icrc2021.desy.de/pf_access_abstracts
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/Presenter-Forum-1-Evening-All-Categories/48
Abstract:
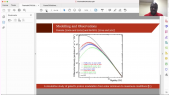
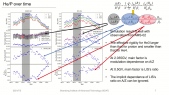
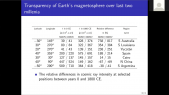
'The space-borne PAMELA experiment was launched on the 15th June 2006 on board the Russian satellite Resurs-DK1 from the Baikonur cosmodrome. From the beginning PAMELA performed high-precision measurements of cosmic rays over a wide energy range until January 2016. Owing to its long-duration operation, PAMELA had turned out to be an optimal detecting apparatus for studies of the solar modulation of cosmic rays over time. The PAMELA collaboration has already published time-dependent proton, Helium and electron spectra as well as the positron to electron ratio over ten years of data. These results are fundamentally important in the fine-tuning of propagation and modulation models of cosmic rays through the Heliosphere.rnrnIn this talk, the yearly average spectra for proton, Deuterium, Helium3 and Helium4 are presented for the 23rd solar minimum (July 2006 - January 2009) and the first part of the 24th solar maximum (until September 2014). The isotopic composition was measured between 0.1 and 1.1 GeV/n using two different detector systems. As expected, the measured spectra display a rising trend towards solar minimum followed by a decreasing trend which has continued as solar maximum approached. The subsequent time-dependent ratio of these isotopes is also presented. rnrnAccording to solar modulation studies, a non-constant ratio is expected due to the different charge-to-mass ratios (and therefore the appropriate rigidities) and the different shapes of the respective local interstellar spectra. Additionally, it is of interest to analyze the observed spectra with state-of-the-art solar modulation models to obtain a deeper understanding of the relative importance of the mechanisms responsible for the propagation of cosmic rays in the Heliosphere over time.'
Authors: Alex Lenni | Mirko Boezio | Riccardo Munini | Wolfgang Menn | Nadir Marcelli | Marius Potgieter | Driaan Bisschoff | Donald Ngobeni | O.P.M Aslam
Collaboration: PAMELA
Indico-ID: 1285
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/1310
Alex Lenni