X-ray emission study of extreme Blazars using AstroSat
-
92 views
-
0 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 10, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 16. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://icrc2021.desy.de/pf_access_abstracts
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/Presenter-Forum-1-Evening-All-Categories/48
Abstract:
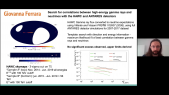
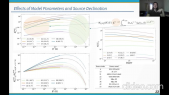
The X-ray spectral curvature in high energy peaked BL Lac (HBL) sources has been interpreted in terms of either shock acceleration, where accelerated electrons attain maximum energy (Lorentz factor, $gamma_{max}$) (Kirk et al.1998,A$and$A,333,452) and consequently emit synchrotron radiation, or due to energy-dependent electron diffusion from the acceleration regions (Goswami et al.2018,MNRAS,480, 2046). However, the X-ray emission features in the extreme class of blazars (EHBLs) are difficult to interpret due to insufficient data at these energies. The high cadence blazar monitoring programme of the *AstroSat*, covering UV to X-ray energy range, has given us unprecedented simultaneous data from the SXT (0.3-10 keV) and the LAXPC (3-80 keV) instruments. This wideband data can be used to constrain a wide range of blazar emission mechanisms.rnrnIn this contribution, we present a detailed spectral and timing study of EHBLs, RGBJ0710+591, 1ES1741+196 and HBL 1ES2322-409 using data from *AstroSat* and simultaneous multi-frequency observations. The *AstroSat* observations of RGBJ0710+591, 1ES1741+196 and 1ES2322-409 were made during 2016, 2019 and 2020 respectively (each with 40ks exposure). The results highlight their X-ray spectral curvature features and the observed considerable shifts in their synchrotron spectral peak energies between different flux states. For RGBJ0710+591, the SXT/LAXPC spectrum shows unusually strong curvature than earlier quasi-simultaneous analysis of *Swift-XRT/NuSTAR* data. We show such a strong curvature can be an outcome of a change in maximum electron energy of the accelerated electrons (Goswami et al. 2020,MNRAS,492,796). We further quantify the X-ray variability of these sources and observe significant variability at longer scales, shown by combined *Swift-XRT* and AstroSat data.'
Authors: Pranjupriya Goswami | Ranjeev Misra | Atreyee Sinha | Rupjyoti Gogoi
Indico-ID: 911
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/961
Pranjupriya Goswami