Non-thermal radio supernova remnants of exiled Wolf-Rayet stars
-
377 views
-
2 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 1, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 20. July 2021 - 12:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/98542982538
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 98542982538
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/46-Supernova-Remnants-GAD-GAI-CRD/76
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-04/5
Abstract:
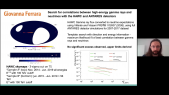
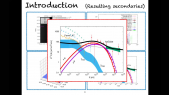
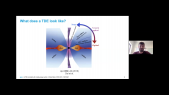
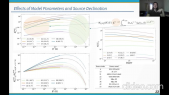
'A signification fraction of Galactic massive stars ($\ge 8\,\rm M_{\odot}$) are ejected from their parent cluster and supersonically sail away through the interstellar medium (ISM). The winds of these fast-moving stars blow asymmetric bubbles thus creating a circumstellar environment in which stars eventually die with a supernova explosion. The morphology of the resulting remnant is largely governed by the circumstellar medium of the defunct progenitor star. In this paper, we present 2D magneto-hydrodynamical simulations investigating the effect of the ISM magnetic field on the shape of the supernova remnants of a $35\, \mathrm M_{\odot}$ star evolving through a Wolf-Rayet phase and running with rnvelocity $20$ and $40\, \rm km\, \rm s^{-1}$, respectively. A $7\, \mu \rm G$ ambient magnetic field is sufficient to modify the properties of the expanding supernova shock front and in particular to prevent the formation of filamentary structures. Prior to the supernova explosion, the compressed magnetic field in the circumstellar medium stabilises the wind/ISM contact discontinuity in the tail of the wind bubble. A consequence is a reduced mixing efficiency of ejecta and wind materials in the inner region of the remnant, where the supernova shock wave propagates. Radiative transfer calculations for synchrotron emission reveal that the non-thermal radio emission has characteristic features reflecting the asymmetry of exiled core-collapse supernova remnants from Wolf-Rayet progenitors. Our models are qualitatively consistent with the radio appearance of several remnants of high-mass progenitors, namely the bilateral G296.5+10.0 and the shell-type remnants CTB109 and Kes~17, respectively.'
Authors: Dominique Meyer | Martin Pohl | Lida Oskinova | Mykola Petrov
Indico-ID: 25
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/982
Dominique Meyer